| Ljubav na djelu | 2014-08-21 |
Musculo-skeletal tumors
They are divided into:
Bone Cancer:
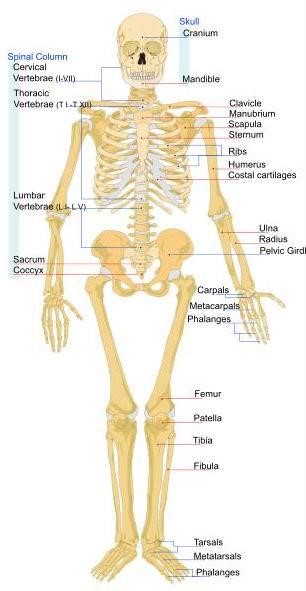
Bone or bone tissue is connectable tissue that supports the body's structure. All the bones in the human body together make up the human skeleton and muscles along with bones make up the organs of movement.
The bones are connected by movable joints and muscles so that the body can run at speeds up to 45 km / h. The bones are solid and strong, hollow inside, so not heavy and make only 14% of our total body weight (lighter than muscle). The bones are not dead substances in the body, and is therefore updated when the fracture. The human skeleton has 206 bones.
Build bones:
1. Firmly bone tissue permeated the canals around which are arranged circularly bone cells, which secrete into the intercellular space of calcium and phosphorus which gives bone strength. Ducts passing blood vessels and nerves.
2. Cartilage is smooth and strong flexible bones and supplement reduces friction in the joint.
3. Spongy bone tissue is bone tissue filled with holes and mottled with small pillars that make bones strong but not too heavy.
4. Periosteum and bone wrapped tightly increment thereto. It was constructed of special connective tissue.
5. Bone marrow - tubular cavities of long bones and cavities in the spongy tissue filled with bone marrow, which produces most of the blood cells.
Primary bone cancer is cancer that develops in the cells of the bone.
The types of primary bone cancer are:
Vrsta raka |
Podrijetlo stanica/tkiva |
Uobičajena lokacija |
Starost |
Osteosarkom |
Osteoid |
Koljena, bedra, nadlaktice |
10-25 |
Hondrosarkom |
Hrskavica |
Zdjelica, bedra, ramena |
50-60 |
Ewingov sarkom |
Nezrelo živčano tkivo (obično u koštanoj srži) |
Zdjelica, bedra, rebra, ruke |
10-20 |
Osteosarcoma and Ewing's sarcoma is most often seen in children and young adults up to 25 years, while chondrosarcoma occurs most frequently in the elderly.
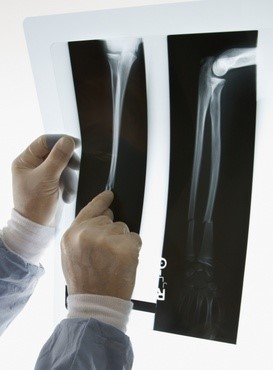
Secondary bone cancer is cancer that has spread to the bones from other parts of the body (eg breast, lung, intestine). Osteosarcoma: Osteosarcoma is the most common bone tumor in children. Mostly occurs in the long bones, such as the upper arm and thigh hands feet, where there is destruction - destruction of the surface layer (periosteum). Osteosarcoma occurs mostly in young people aged between 10 and 25 years, and are more common in male than in female patients. Patients complain of pain, sometimes swelling of the diseased bone, which is often mistakenly attributed to accidents. Diagnosis can be difficult because the disease can be replaced with local infections, the consequences of injuries, arthritis, lack of vitamins or a benign tumor. Although osteosarcoma can be detected by X-ray images, however, the diagnosis must be set by biopsy of affected bone. As in diagnosing the disease may be present and metastases (eg lung), before treatment is necessary to make the time by CT. In the treatment of osteosarcoma chemotherapy is used, and then the operation. Today in many cases can avoid amputation. At the hospital the doctors will discuss with you about the possibility which is correct for your child.
 Causes and risk factors:
Causes and risk factors:
There is no clearly defined cause of osteosarcoma, although there is a tendency that this tumor occurs within the family. Likewise, there are no known predisposition for the development of osteosarcoma.
Diagnosing
Persons who was later diagnosed with osteosarcoma, a doctor can occur with the following simptoms:
How valuable time would not be wasted on the wrong diagnosis and treatments, it is necessary to x-ray the areas affected by osteosarcoma. Once the X-rays confirming the existence of the tumor, followed by computerized tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging scan (MRI) or positron emission tomography (PET). Also, the specialist may perform a biopsy to determine what kind of cell type works. Location, size and extent of tumor affecting the selection and the outcome off treatment. Treatment for the treatment of osteosarcoma in charge of the professional clinical staff, specialist orthopedic surgeons and oncologists. Chemotherapy can shrink the tumor and treat possible metastasis, such as the lungs. Following, possible surgical operation limb or affected area, in order to prevent amputation. Reconstructive surgery may also be an option, and may include a series of operations to reimplantend on or implanted prosthesis. Scan in some cases, after chemotherapy is not possible operations. In others, there are types of operations that are possible, but they can weaken the body. In such situations, consider the radiation, especially if the biopsy showed that it is a specific type of cell. It should be prepared for possible complications of the treatment, as well as side effects such as wound infection, pain and nausea. The outcome of treatment depends largely on the stage of diagnosed with osteosarcoma, the skill of the doctors and medical staff, and the ways of treating cancer. If the disease is detected relatively early and treated properly, the chances of survival exceeding 90 percent. In the case of aggressive forms of cancer, which began metastasize, the chances of survival are 50 percent. However, accurate forecasts cannot be made because each patient responds differently to treatment.
Ewing's sarcoma
Ewing's sarcoma is a malignant bone tumor that was first described in the literature James E wing 1921st year. Ewing's sarcoma usually occurs in childhood or early adolescence, with the highest incidence between 10 and 20 years of age, although it can occur in younger and older age. The most frequently occurs in the pelvis, thigh and upper arm bones and ribs. Ewing's sarcoma is the most frequent occurrence of other tumor of bone tissue in children and malign bone tumors in children. The incidence of illness was 0.3 patients per 1 million children younger than 3 years and 4.6 children in one million young people between 15 and 19 years of age. The average incidence of illness was less than 2 patients at one million children a year. The ratio of male and female children suffer is 1.5:1. Survival in localized tumors is 60-70% of patients, 30% survival with lung metastases and survival by less than 10% with metastases at other sites.
James Ewing Ewing's sarcoma is described as a tumor of flat and long bones susceptible to radiation. For this malignant tumor with undifferentiated small round cells to the 1980s was thought to have Endothelial origin, but recent data suggest that it is probably a najnezrelijoj station from neuroektoderma (postganglijskih parasympathetic cholinergic neurons). Although bone cancer, Ewing's sarcoma can arise in soft tissues - extraosseous Ewing's sarcoma (EES) or can occur as a differentiated form known as peripheral primitive neuroekodermalni tumor (PPNET). Therefore, it is generally accepted term "Ewing sarcoma family of tumors" (ESFT).
The tumor causes local bone pain or swelling of soft tissue. It is located on the diaphysis of long bones (femur), and the flat bones of the trunk (vertebrae, ribs, pelvic bone). It is more common in the second decade of life (75% are diagnosed before 20 years of life and 90% before 30 years). Unlike osteosarcoma often have intermittent fever, and there are other systemic symptoms: weight loss, weakness and fever, which also indicate metastasis. Approximately 25% of patients have at the beginning of the disease matogenous metastases in the lungs, bones, bone marrow, or pleura. X-rays show the tumor diaphysis extending to the metaphysis. There are mixed lytic and sleroz defects, or buildings with new bone formation. About ⅔ patients has tumor mass consisting of soft tissue, and sometimes pathological fractures.
Cytogenetic and molecular analysis of tumor tissues show five reciprocal translocation of t which is the most common (11, 22) (q24, q12) that results in a fusion gene EWS-FLI1 - (90 to 95% of the tumor) and is followed by the frequency of t (21; 22 ) (q22, q12), which results in a fusion gene EWS-ERG (5-10% of the tumor). RT-PCR and FISH infection can be detected specific transcripts of the EWS-FLI1 and EWS-ERG expressing tumors. These methods will facilitate the diagnosis, which is so far due to the lack of specific pathological images based mainly towards the site of a tumor and the exclusion of other small round cell tumors.
CT lung and bone scintigraphy with technetium is necessary to search for metastasis. The need to evaluate the bone marrow. Computerized tomography bone on which there is a primary tumor provides valuable information on the extension of the disease in soft tissue and medullary cavity, which is important when planning a surgery in which bone is removed along with keeping the extremities. Specifically Ewing's sarcoma spreads from the bone in which it arises through the medullary canal, or penetrates the cortex and spreads into the surrounding soft tissue, infiltrate surrounding muscle and fascia often passes along and through the proximal joint.
Survival rate of 15% was to treat with surgery and radiation therapy as an isolated method had even worse results than about 10%. Ewing's sarcoma is necessary to treat a systemic disease tz. a combination of surgery, radiation and chemotherapy to control the primary tumor, and to eradicate distant metastases. The surgery should not be too mutilirajući. Amputated the distal fibula, tibia, talus and calcaneus. Tumors fingers and small tarsal and metatarsal bones treated hemiamputation of the feet. Tumors ribs, clavicle and scapula are widely excised, usually after preoperative administration of cytostatics. The proximal tibia, radius and femur is not amputated unless they are very destructed.
Radiates the entire length of the affected bone with 6000-7000 cGy but how these doses lead to severe damage f in combination with chemotherapy can be reduced to 4000-5000 cGy without prejudice to the final outcome. "VACA", "video", "VAI" and similar programs cytostatic treatment recommended by the Intergroup Ewing's Sarcoma Study (IESS) and Cooperative Ewing's Sarcoma Study (CESS). EURO-E.W.I.N.G. 99 of Survival with such a combination therapy ranges from 55-65% rhabdomyosarcoma It occurs in muscle cells. It is more common in boys than in girls, mostly in the age between 2 and 6 years. Although it can occur in any muscle tissue, usually occurs in the head and neck, pelvis and extremities. Rhabdosarcom rapidly growing and expanding. Symptoms are thankfully easier to show than for most other types of tumors in childhood. Mainly notice the island or palpable node. Other symptoms depend on the tumor location. If it grows, for example in the area of the eye then eyesight weakens. If attacked by the throat can cause problems in swallowing. Ensures accurate diagnosis of tumor biopsy tissue attacked. With the help of ultrasound, X-ray image, scintigraphy, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), lumbar puncture and bone marrow metastases are excluded. The therapy uses a combination of surgery, chemotherapy and radiation. If the tumor is large or has given metastases first given chemotherapy and radiation, to try to reduce the tumor to a certain size, it can easily be surgically removed. Approximately 60-70% of children heal.